用自动化构建方式commenjs规范写vuejs
首先创建合理的项目开发目录结构
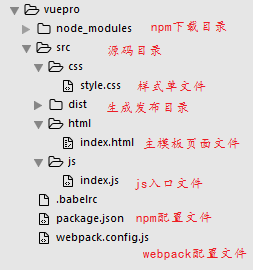
初始化 package.json 文件和创建 .babelrc 编译es2015语法文件,以及npm 安装vue相关插件
|
|
先装这些,以后继续添加,webpack 不建议全局安装,版本更新问题
package.json
webpack.config.js
.babelrc
接下来就可以开始正式写页面代码了
在src/html/index.html 里面写页面代码,在 src/js/index.js 里面写页面主逻辑
|
|
|
|
在 package.json 里设置启动webpack
|
|
运行项目
用组件化开发
可复用的结构html代码可以封装成组件的形式,挂载在非body的根节点上
安装vue-loader 并配置可识别.vue 文件
分为全局注册和局部注册
|
|
html 结构
全局注册
|
|
局部注册
方式一
|
|
方式二 在src目录下创建 components 组件文件夹,新建mycomponents.vue 文件
|
|
|
|
父子组件之间的通信
每一个组件都有独立的作用域,通过props 值传递参数
Props验证
子组件访问其相邻的兄弟组件
通过this.$parent.$children 获取其父组件下所有的子组件(数组);可通过数组索引,也可以给子组件增加一个索引id ref:name 访问
|
|
父子组件嵌套
|
|
webpack配置热加载免刷新
使用webpack-dev-server 是一个小型静态服务器搭建热运行环境,代码修改无需编译和页面刷新进行预览,并不产生任何编译文件,在内存当中运行
安装 webpack-dev-server 并配置
|
|
运行服务
使用 webpack –config webpack.dev.config.js 指定要运行的webpack 配置文件
|
|
路由插件
简单理解路由就是单页面应用跳转链接的管理
安装
使用cdn https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js 方式加载在vue后面
|
|
如果在一个模块化工程中使用它,必须要通过 Vue.use() 明确地安装路由功能:
|
|
配置路由映射
|
|
模板中使用
|
|
使用 <router-link> 组件支持用户在具有路由功能的应用中(点击)导航。 通过 to 属性指定目标地址,默认渲染成带有正确链接的 <a> 标签,可以通过配置 tag 属性生成别的标签.。另外,当目标路由成功激活时,链接元素自动设置一个表示激活的 CSS 类名 .router-link-active
|
|
使用 <router-view></router-view> 组件是一个 functional 组件,渲染路径匹配到的视图组件。如果 <router-view>设置了名称,则会渲染对应的路由配置中 components 下的相应组件。
任何插件使用先引入然后用Vue.use()
使用 vue-resource ajax请求插件,引入加载之后会在全局注册一个$http 的变量
|
|
ajax获取后台新闻内容展示到页面,在php后端接口数据有newsid 字段,根据这个字段进行传值,用 <router-link> :to 根据命名路由,通过params带有newsid 参数传值。在detail页面初始化生命周期函数里 用get方式接收地址后带有 this.$route.params 的参数,回调对应的条目,赋值到newsdetail 数据中。然后渲染到页面
|
|
自定义插件
自定义插件的意义在于把业务代码写到插件中,多组件可服用。避免写在组件中显得冗余。
自定义一个插件必须包含一个公开方法 install 这个方法的第一个参数是 Vue 构造器 ,第二个参数是一个可选的选项对象
|
|
使用 Vue.prototype 定义插件全局对象方法,在组件中直接 this.$xx 调用
|
|
在自定义插件中定义自定义指令
使用 v-ckname 绑定指令
|
|
使用 extend 创建元素并手动挂载,和创建普通的组件格式一样,然后要实例化,$mount 挂载在元素上
|
|
Vuex 状态管理插件
|
|
使用 getters 对原始数据进行过滤
|
|
Actions 类似于 mutation
Action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
可以在 actions 内部执行异步操作
|
|
分发 actions 相当于触发mutation
|
|
Modules 将 store 分割到模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getters。
遵循项目结构
通过导出的形式写单独的一个module模块
引用
修改组件中的调用方法
|
|
使用fecth
|
|